Takeaways
- Privacy coins are cryptocurrencies that hide transaction details to enhance user anonymity.
- They use technologies like ring signatures, stealth addresses, and zk-SNARKs to hide sender, receiver, and transaction amounts.
- Top privacy coins like Monero and Zcash offer different approaches to achieve on-chain privacy.
- Use cases range from protecting personal finances and confidential business transactions to enabling anonymous donations and activism.
- The legal status of privacy coins varies by country, with some jurisdictions imposing restrictions or bans due to regulatory concerns.
Cryptocurrencies were born with the promise of decentralization and financial freedom. But not all crypto is created equal when it comes to privacy.
While Bitcoin and Ethereum transactions are permanently recorded on public ledgers, privacy coins offer something radically different: anonymity.
Privacy coins are a category of cryptocurrencies designed to conceal transaction details, including sender and receiver identities and transaction amounts. In a world where every blockchain transfer can be traced and linked, these coins provide a powerful layer of personal financial privacy.
But why is this important?
From individuals seeking financial sovereignty to businesses protecting trade secrets, the demand for anonymous cryptocurrencies is growing. And as governments tighten regulations and blockchain analytics grow more sophisticated, privacy coins are stepping into the spotlight.
What Are Privacy Coins and What Makes A Coin “Private”?
Privacy coins are digital currencies that provide user anonymity through cryptography to ensure transaction details stay unobservable.
The core design element differentiates them from transparent cryptocurrencies.
Also Read: Coin vs. Token - What’s the Difference?
Think of Bitcoin’s blockchain as a public bulletin board. Here, every transaction is posted for all to see. That means anyone can dig into who sent what to whom and which digital addresses were involved. Although your real name isn't directly attached, your entire transaction history is an open book if someone identifies your address. This is pseudonymity, not true privacy.
A coin becomes “private” by concealing specific transaction components like:
- The identity of any transaction sender
- The final destination receiver address
- The specific transaction value
This data obscurification empowers users with control over financial data and on-chain activities. It prevents the tracing of funds between involved transaction parties. Users gain anonymity in their digital financial interactions.
Also Read: What Is BTCFi? Bitcoin's Decentralized Finance Landscape
How Is Privacy Different From Anonymity?
Privacy and anonymity are not synonymous.
Privacy is about agency. It’s the power to choose what to disclose, when, and to whom. In privacy-preserving systems, your data exists—but it’s shielded from public exposure unless you decide to reveal it. Think of it as encryption with intent. Technologies like zero-knowledge proofs and view keys offer users a way to remain private without being invisible.
Anonymity is about erasure. It’s the deliberate removal of identity from the equation altogether. In anonymous systems, transactions occur without any traceable link to an individual or even a pseudonym. There’s no reveal key or trail.
Privacy |
Anonymity |
|
|
Goal |
Control over information sharing |
Total untraceability |
|
User Choice |
Opt-in sharing (e.g., view key) |
No identity tied at all |
|
Visibility |
Hidden data, but potentially revealable |
Not linked to any identity |
|
Example |
Monero (private but verifiable) |
Using Bitcoin via mixer and Tor combo |
How Privacy Coins Work (Technical Breakdown)
Privacy tech is a work in progress, aiming to outpace those trying to peek behind the curtain. To date, six core technologies power modern privacy coin systems:
1. Ring Signatures
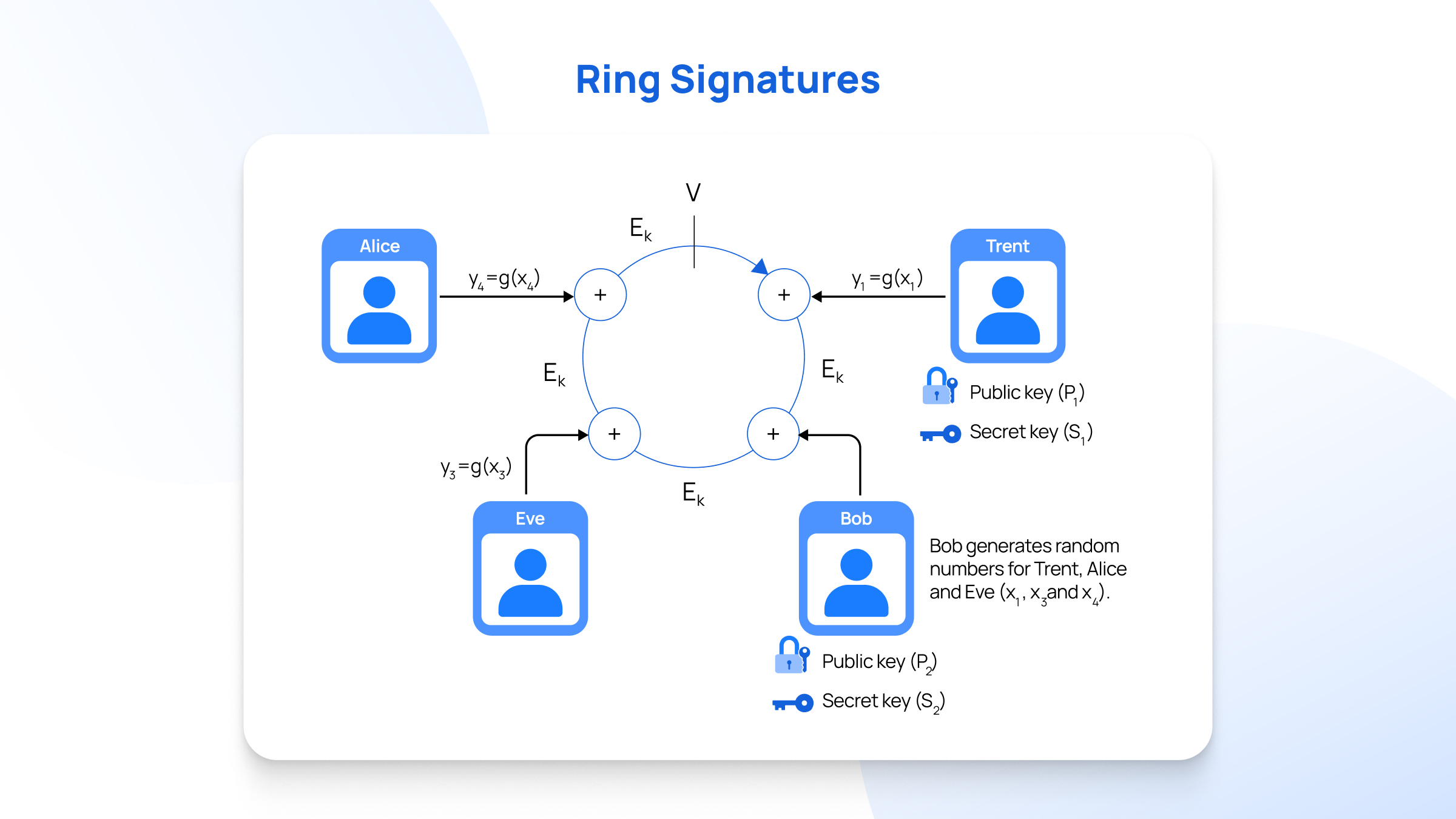
Ring signatures combine multiple signatures to protect the sender's identity. The system mixes user transactions with decoy transactions. This creates a "ring" of possible signers.
Observers see "either A or G or K or P" instead of "definitely A". The transaction remains verifiable without revealing the actual sender. Monero implements ring signatures for sender anonymity.
2. zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Proofs)
%20(1).jpg)
zk-SNARKs allow transaction verification without revealing sensitive information. Users prove transaction validity without exposing details. The system verifies amounts and ownership without disclosure.
Zcash employs zk-SNARKs to encrypt transaction data. Users choose between transparent and shielded transactions. This technology provides stronger anonymity guarantees than ring signatures.
3. CoinJoin
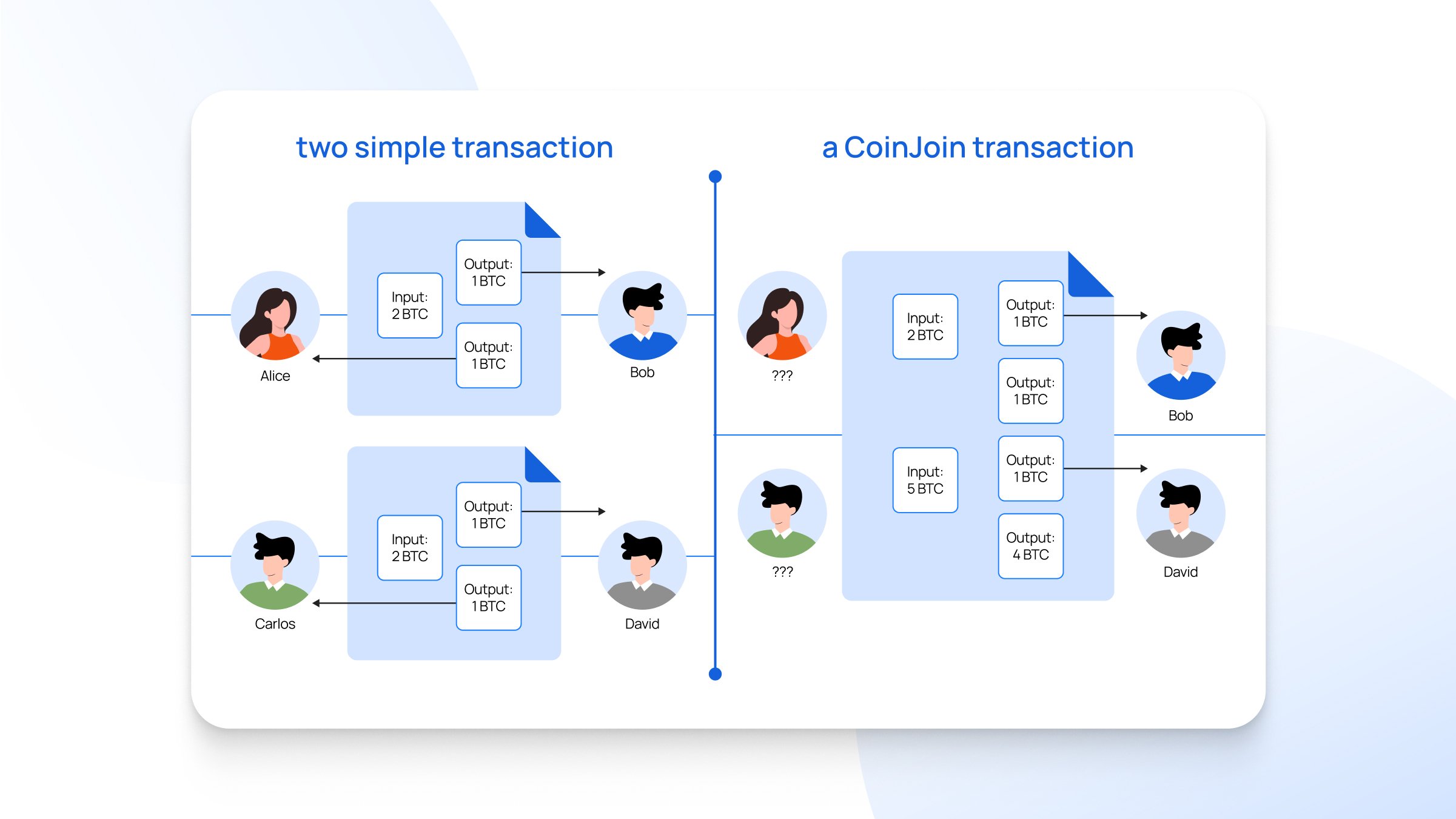
CoinJoin combines payments from various senders into single transactions. Multiple inputs merge under one transaction structure. This mixer conceals the sender by merging different participants.
The system makes tracing transaction trails nearly impossible for outsiders. Bitcoin mixing services implement CoinJoin protocols. The technique reduces blockchain storage requirements.
4. MimbleWimble
MimbleWimble integrates Confidential Transactions, CoinJoin, and Cut-Through protocols. The system combines different inputs with outputs and signature data. Cut-Through removes redundant transaction data from blocks.
Transactions use one-time addresses that are invisible on public blockchains. Transactions within blocks appear as random input and output mixes. Grin and BEAM implement MimbleWimble protocols.
5. Dandelion++
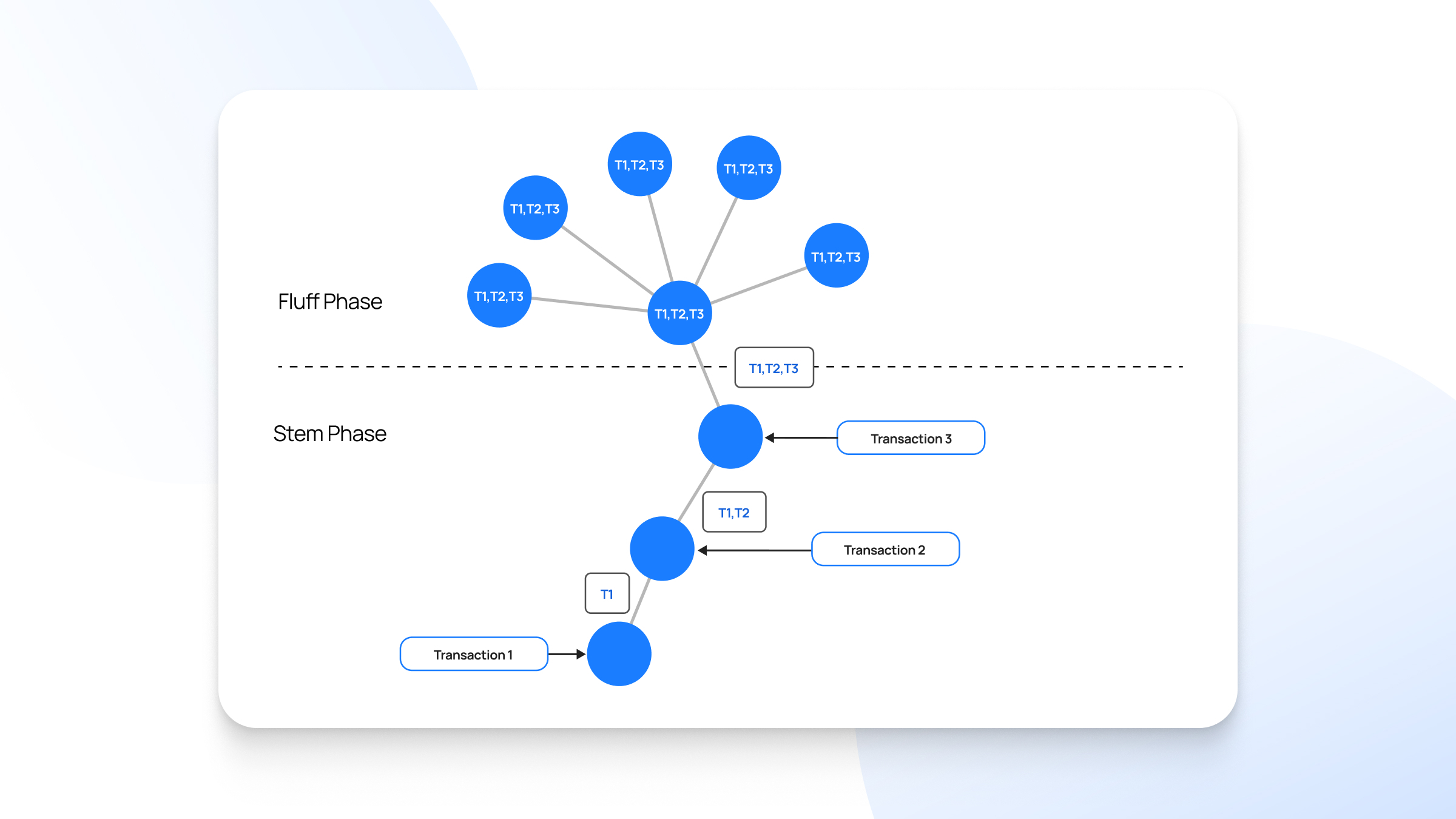
Dandelion++ defends against de-anonymization attacks during transaction propagation. The protocol operates in two phases: stem and fluff.
Stem phase relays transactions to single random peers. Fluff phase broadcasts transactions like ordinary diffusion. This prevents attackers from linking transactions to IP addresses.
Privacy coins combine these technologies for comprehensive anonymity. Each method addresses specific privacy vulnerabilities in blockchain systems.
Top 6 Privacy Coins For 2025
These top privacy coins are the key players in the anonymity game heading into 2025.
Note: This list is neither exhaustive nor a recommendation. Do your own research before investing.
1. Monero (XMR)
Monero makes privacy mandatory. Every single transaction uses ring signatures, stealth addresses, and RingCT (which hides amounts) by default. You can't accidentally send a public transaction. It's known for its strong community and unwavering focus on anonymity.
- Privacy Tech: Ring Signatures, Stealth Addresses, RingCT
- Key Feature: Privacy isn't optional, it's baked in
2. Zcash (ZEC)
Zcash offers "optional privacy" using its groundbreaking zk-SNARKs. You can send fully "shielded" (private) transactions or "transparent" (public) ones. This choice can help with usability and regulation, but means not all Zcash is anonymous.
- Privacy Tech: zk-SNARKs (for shielded)
- Key Feature: You can choose your privacy level
3. Firo (FIRO)
Formerly Zcoin, Firo uses its Lelantus Spark protocol to let users effectively "burn" their coins and "redeem" new ones with no history attached. It also uses Dandelion++ to hide IP addresses.
- Privacy Tech: Lelantus Spark, Dandelion++
- Key Feature: Focuses on breaking transaction history links
4. Dash (DASH)
Dash primarily focuses on being a fast and user-friendly digital cash. It offers an optional privacy feature, PrivateSend, which uses CoinJoin mixing. It's less robust than Monero or Zcash but offers a quick mixing solution.
- Privacy Tech: PrivateSend (CoinJoin)
- Key Feature: Optional privacy; focuses on speed
5. Grin (GRIN)
Grin runs on the MimbleWimble protocol, a design that inherently offers privacy and makes the blockchain much smaller. There aren't even traditional addresses. Privacy is the default, and it's known for its pure, community-driven vibe.
- Privacy Tech: MimbleWimble
- Key Feature: Radical design, default privacy, no addresses
6. Secret Network (SCRT)
Secret isn't just about private payments; it's about private computations. It allows for "secret smart contracts" where encrypted data is used and stored. This opens the door for private decentralized applications (dApps).
- Privacy Tech: Encrypted Smart Contracts
- Key Feature: Privacy for dApps and data, not just transactions
Key Use Cases of Privacy Coins
So, who needs these privacy coins? It’s not just for people wearing trench coats and dark glasses.
- Personal Financial Privacy: Don’t want your boss, your girlfriend, or your best bud to know your salary intricacies, spending habits, or how much crypto you hold? Privacy coins keep your financial life private.
- Business Confidentiality: Companies can use them for payroll or B2B payments without broadcasting sensitive financial data to competitors.
- Charitable and Political Support: Donating to controversial or sensitive charities or political groups without attracting unwanted attention.
- Financial Freedom in Restrictive Environments: In places where financial freedom is restricted, privacy coins can be a vital tool for economic survival and activism.
- Making Money Equal (Fungibility): If a Bitcoin was once used for something shady, it can become "tainted" and hard to use. Privacy coins aim to make every coin identical and untraceable, just like every dollar bill is worth a dollar, regardless of where it's been.
Privacy Coins vs Privacy Tools: A Comparative Outlook
Privacy cryptocurrency has privacy built-in, while privacy tools try to add it onto transparent coins like Bitcoin.
Feature |
Privacy Coins (e.g., Monero) |
Privacy Tools (e.g., Mixers for Bitcoin) |
|---|---|---|
|
Privacy Level |
Generally higher, often mandatory. |
Varies greatly; can be strong but relies on the tool and user numbers. |
|
Mechanism |
Baked into the coin's code (zk-SNARKs, etc.). |
External services or software that shuffle coins (CoinJoin, etc.). |
|
Ease of Use |
Usually seamless—just send the transaction. |
Needs extra steps, trusting a third party, and potential fees. |
|
Fungibility |
Stronger—coins have no public history. |
Aims to improve it, but mixed coins can sometimes be flagged. |
|
Trust |
Trust in the math and the code. |
Often requires trust in the mixer operator (who could log or steal). |
|
Regulatory Risk |
Coins face delisting/bans. |
Mixers are a major target for regulators (e.g., Tornado Cash). |
Are Privacy Coins Legal?
Here’s the tricky part. The answer is: "It depends." The legal status of privacy coins is a confusing, shifting map.
1. Regulatory Challenges
Financial authorities cite anti-money laundering compliance challenges, as privacy coins' anonymity features complicate user identification and transaction monitoring. Law enforcement agencies struggle to trace illicit activities and gather evidence for legal proceedings. It makes their job (and exchanges trying to follow the rules) much harder.
2. Exchange-Level Restrictions
Major exchanges, including Bittrex, Kraken, and Huobi, have voluntarily delisted privacy coins. The U.S. Treasury lifted sanctions on the 2022 Tornado Cash mixing protocol, meaning privacy coins are still legal in the country. Yet, all of this makes them harder to buy and sell.
3. Outright Bans
Japan banned privacy coins entirely in 2018, while South Korea and Australia prohibit exchanges from offering them. Dubai joined this group in 2023. The EU will also ban privacy coins and anonymous crypto accounts starting July 2027 under the new Anti-Money Laundering Regulation.
Closing Thoughts
To sum up, the future of privacy coins is a tug-of-war between technology, user demand, and regulation. They offer a powerful promise of digital cash, but navigating their world requires understanding both the tech and the ever-present regulatory risks.
FAQs
- Are privacy coins illegal?
The legality of privacy coins depends on the jurisdiction. In most countries, holding or using them is not illegal, but exchanges may delist them due to regulatory pressure and AML (anti-money laundering) rules.
- Can privacy coins be traced?
Privacy coins like Monero and Zcash (when shielded) use technology designed to make transactions untraceable. However, law enforcement agencies and analytics firms are developing tools to analyze patterns, though full traceability remains limited.
- What is the difference between privacy coins and Bitcoin?
Bitcoin transactions are public and traceable on the blockchain, while privacy coins offer enhanced anonymity by obscuring or encrypting key details of each transaction.
- Is Bitcoin not private?
Bitcoin is not private as all transactions are recorded on a public ledger that anyone can view. While wallet addresses aren’t tied to real names by default, they can often be traced back to individuals through blockchain analysis and data leaks.
- Why are privacy coins controversial?
Critics argue that privacy coins can be used for illegal activities such as money laundering or tax evasion. Supporters argue they are essential for financial freedom, privacy rights, and protection against surveillance.
- Are privacy coins banned anywhere?
Yes. Countries like Japan and South Korea have banned or heavily restricted privacy coins due to AML concerns. Other regions may impose reporting obligations on their use.
- Can privacy coins be used for everyday transactions?
Yes, privacy coins can be used like any other crypto for peer-to-peer payments, online purchases, and donations. However, merchant adoption is lower due to regulatory uncertainty.






