Stablecoins are no longer just a trader’s haven. They’ve become programmable, interoperable money powering payments, settlements, and financial automation across industries.
With regulatory clarity from frameworks like the GENIUS Act (US), MiCA (EU), and VARA (UAE), stablecoins are moving from crypto-native tools to global settlement infrastructure.
Here are the ten most impactful use cases reshaping global finance beyond trading.
1. Cross-Border Remittances
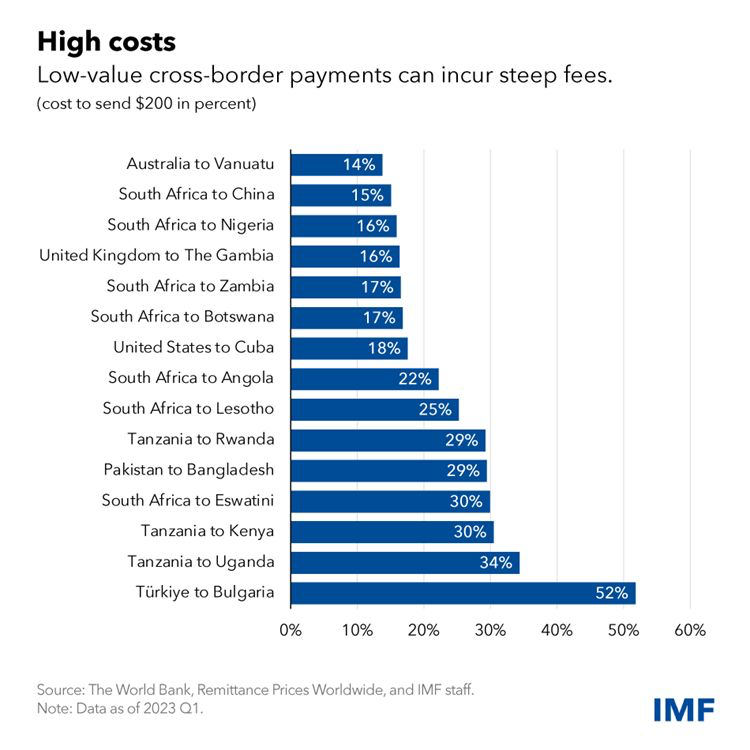
Traditional remittances remain expensive and slow. According to the World Bank, sending $200 costs an average of 6.6%, with transfers taking days. Stablecoins solve both problems.
By enabling peer-to-peer transfers via mobile wallets, they eliminate correspondent banks and reduce transaction times to seconds.
Source: LinkedIn
Platforms like MoneyGram (with Stellar), Minipay (by Opera), and Transak’s off-ramp integrations already use stablecoins to move money across borders. These platforms bridge the 1.4 billion unbanked adults who have mobile access but no bank account.
2. Enterprise Treasury & Liquidity Management
For global enterprises, treasury operations are complex. It involves managing cash across multiple subsidiaries, currencies, and banks, which introduces cost and delay. Stablecoins simplify this through real-time cash management, on-chain reconciliation, and programmable liquidity flows.
Companies can use stablecoins for intercompany settlements, automate cash pooling, and even earn regulated yield through tokenized treasuries such as ONDO and BUIDL.
3. Online Payments & E-Commerce
E-commerce payment rails rely on intermediaries and charge hefty fees (1.5–3.5%). Stablecoins offer a cheaper, faster, and fraud-resistant alternative. They (stablecoins) bring instant settlement, no chargebacks, and global accessibility that’s perfect for cross-border sellers.
Shopify’s Solana Pay integration allows merchants to accept USDC directly, while payment processors like Transak and Coinbase Commerce offer instant fiat conversions for businesses that want to stay compliant but crypto-ready.
4. On-Chain DeFi and Lending
Stablecoins form the base layer of decentralized finance. They act as collateral, liquidity, and unit of account across protocols like Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO. Users can borrow against volatile assets, earn yield in stablecoin pairs, and participate in governance or liquidity provisioning, all without relying on traditional intermediaries.
As DeFi integrates real-world assets (RWAs) such as T-bills and bonds, stablecoins become even more critical as settlement assets bridging TradFi and on-chain markets.
Also Read: How RWA Tokenization Unlocks Decentralized Loans?
5. RWA Settlement and Tokenization
The next trillion-dollar wave lies in tokenizing real-world assets, like treasuries, bonds, real estate, and credit. Stablecoins act as the settlement currency for these tokenized instruments.
With platforms like Centrifuge, Maple, and Ondo, investors can buy fractionalized real-world assets directly on-chain and settle in stablecoins like USDC or DAI.
McKinsey estimates tokenized markets could reach $4 trillion by 2030, making stablecoins the “cash leg” of the new digital asset ecosystem.

Source: McKinsey
6. Merchant Payouts and B2B Transfers
Businesses depend on smooth payouts to suppliers, freelancers, or partners. But banking hours, cut-offs, and FX fees slow things down. Stablecoins enable instant B2B transfers globally, reducing both time and cost.
Stripe’s “Pay with Crypto”, powered by Paxos, lets businesses settle merchant earnings in stablecoins instantly. Similarly, Visa Direct and Transak Off-Ramp now allow instant fiat withdrawals from stablecoin balances.
7. Charitable Aid & Humanitarian Relief
Stablecoins are radically improving how humanitarian aid is distributed. Instead of routing funds through intermediaries, NGOs can send digital dollars directly to wallets, ensuring transparency and speed.
The UNHCR has already delivered aid in USDC on the Stellar network to Ukrainian refugees. This model ensures traceability, reduces administrative overhead, and provides instant access to funds for those who need them most.
8. Programmable Invoicing & Conditional Payments
Stablecoins unlock programmable finance through smart contracts. Payments can be tied to specific conditions, say, shipment delivery, milestone completion, or time locks. This automation eliminates disputes, reduces fraud, and enhances trust between parties.
In supply chain finance, for instance, a payment can automatically trigger when goods reach customs clearance, all verified on-chain.
9. Interbank & Institutional Settlement Layers
Large financial institutions are now experimenting with stablecoins as interbank settlement assets, replacing traditional SWIFT-based flows.
Examples include JPMorgan’s JPM Coin, Ripple’s RLUSD, and PayPal’s PYUSD. All these are designed for institutional-grade settlements.
These systems allow instant cross-border liquidity between banks and fintechs, creating a parallel real-time settlement layer for fiat-backed digital money.
10. AI Agent & Machine-to-Machine Payments
Many argue that the next frontier for finance is autonomous payments between machines and AI agents.
Stablecoins allow devices, APIs, or digital agents to transact without human input. Think self-driving cars paying tolls or cloud AI models buying compute power.
Since stablecoins operate 24/7 and are programmable, they’re ideal for autonomous, micro, and recurring transactions that the traditional banking system cannot handle.
Conclusion
Stablecoins went from being crypto’s risk hedge to the universal money layer of the internet.
As stablecoin infrastructure matures through banking integrations, tokenized assets, and regulatory frameworks, it’s clear they are becoming the foundation of finance itself.






